1. DWM1000 거리측정 방법
DWM1000을 이용한 거리측정 방법은 타임스탬프를 포함하는 통신 패킷을 다른 모듈로 전송하고 응답되는 시간을 측정하여 시각차이를 측정하여 거리를 계산하는 방식이다.
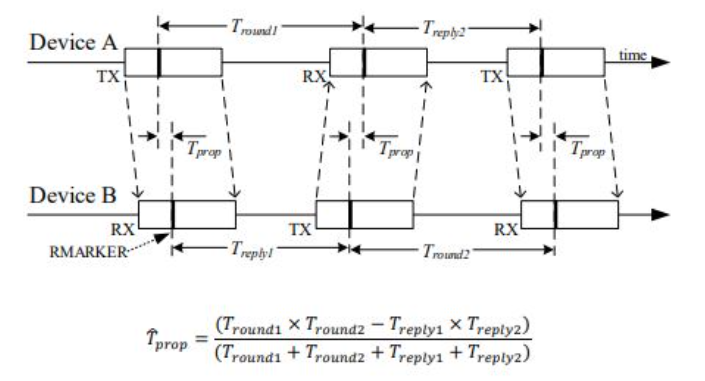
2. 거리측정 샘플프로그램
2-1 앵커 모듈용(신호응답)
/*
* MIT License
*
* Copyright (c) 2018 Michele Biondi, Andrea Salvatori
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
* copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
* SOFTWARE.
*/
/*
* Copyright (c) 2015 by Thomas Trojer <thomas@trojer.net>
* Decawave DW1000 library for arduino.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
* @file RangingTag.ino
* Use this to test two-way ranging functionality with two DW1000Ng:: This is
* the tag component's code which polls for range computation. Addressing and
* frame filtering is currently done in a custom way, as no MAC features are
* implemented yet.
*
* Complements the "RangingAnchor" example sketch.
*
* @todo
* - use enum instead of define
* - move strings to flash (less RAM consumption)
*/
#include <DW1000Ng.hpp>
#include <DW1000NgUtils.hpp>
#include <DW1000NgTime.hpp>
#include <DW1000NgConstants.hpp>
/*
// connection pins
const uint8_t PIN_RST = 9; // reset pin
const uint8_t PIN_IRQ = 2; // irq pin
const uint8_t PIN_SS = SS; // spi select pin
*/
const uint8_t PIN_SCK = 18;
const uint8_t PIN_MOSI = 23;
const uint8_t PIN_MISO = 19;
const uint8_t PIN_SS = 2;
const uint8_t PIN_RST = 15;
const uint8_t PIN_IRQ = 5;
// messages used in the ranging protocol
// TODO replace by enum
#define POLL 0
#define POLL_ACK 1
#define RANGE 2
#define RANGE_REPORT 3
#define RANGE_FAILED 255
// message flow state
volatile byte expectedMsgId = POLL_ACK;
// message sent/received state
volatile boolean sentAck = false;
volatile boolean receivedAck = false;
// timestamps to remember
uint64_t timePollSent;
uint64_t timePollAckReceived;
uint64_t timeRangeSent;
// data buffer
#define LEN_DATA 16
byte data[LEN_DATA];
// watchdog and reset period
uint32_t lastActivity;
uint32_t resetPeriod = 250;
// reply times (same on both sides for symm. ranging)
uint16_t replyDelayTimeUS = 3000;
device_configuration_t DEFAULT_CONFIG = {
false,
true,
true,
true,
false,
SFDMode::STANDARD_SFD,
Channel::CHANNEL_5,
DataRate::RATE_850KBPS,
PulseFrequency::FREQ_16MHZ,
PreambleLength::LEN_256,
PreambleCode::CODE_3
};
interrupt_configuration_t DEFAULT_INTERRUPT_CONFIG = {
true,
true,
true,
false,
true
};
void setup() {
// DEBUG monitoring
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println(F("### DW1000Ng-arduino-ranging-tag ###"));
// initialize the driver
DW1000Ng::initialize(PIN_SS, PIN_IRQ, PIN_RST);
Serial.println("DW1000Ng initialized ...");
// general configuration
DW1000Ng::applyConfiguration(DEFAULT_CONFIG);
DW1000Ng::applyInterruptConfiguration(DEFAULT_INTERRUPT_CONFIG);
DW1000Ng::setNetworkId(10);
DW1000Ng::setAntennaDelay(16436);
Serial.println(F("Committed configuration ..."));
// DEBUG chip info and registers pretty printed
char msg[128];
DW1000Ng::getPrintableDeviceIdentifier(msg);
Serial.print("Device ID: "); Serial.println(msg);
DW1000Ng::getPrintableExtendedUniqueIdentifier(msg);
Serial.print("Unique ID: "); Serial.println(msg);
DW1000Ng::getPrintableNetworkIdAndShortAddress(msg);
Serial.print("Network ID & Device Address: "); Serial.println(msg);
DW1000Ng::getPrintableDeviceMode(msg);
Serial.print("Device mode: "); Serial.println(msg);
// attach callback for (successfully) sent and received messages
DW1000Ng::attachSentHandler(handleSent);
DW1000Ng::attachReceivedHandler(handleReceived);
// anchor starts by transmitting a POLL message
transmitPoll();
noteActivity();
}
void noteActivity() {
// update activity timestamp, so that we do not reach "resetPeriod"
lastActivity = millis();
}
void resetInactive() {
// tag sends POLL and listens for POLL_ACK
expectedMsgId = POLL_ACK;
DW1000Ng::forceTRxOff();
transmitPoll();
noteActivity();
}
void handleSent() {
// status change on sent success
sentAck = true;
}
void handleReceived() {
// status change on received success
receivedAck = true;
}
void transmitPoll() {
data[0] = POLL;
DW1000Ng::setTransmitData(data, LEN_DATA);
DW1000Ng::startTransmit();
}
void transmitRange() {
data[0] = RANGE;
/* Calculation of future time */
byte futureTimeBytes[LENGTH_TIMESTAMP];
timeRangeSent = DW1000Ng::getSystemTimestamp();
timeRangeSent += DW1000NgTime::microsecondsToUWBTime(replyDelayTimeUS);
DW1000NgUtils::writeValueToBytes(futureTimeBytes, timeRangeSent, LENGTH_TIMESTAMP);
DW1000Ng::setDelayedTRX(futureTimeBytes);
timeRangeSent += DW1000Ng::getTxAntennaDelay();
DW1000NgUtils::writeValueToBytes(data + 1, timePollSent, LENGTH_TIMESTAMP);
DW1000NgUtils::writeValueToBytes(data + 6, timePollAckReceived, LENGTH_TIMESTAMP);
DW1000NgUtils::writeValueToBytes(data + 11, timeRangeSent, LENGTH_TIMESTAMP);
DW1000Ng::setTransmitData(data, LEN_DATA);
DW1000Ng::startTransmit(TransmitMode::DELAYED);
//Serial.print("Expect RANGE to be sent @ "); Serial.println(timeRangeSent.getAsFloat());
}
void loop() {
if (!sentAck && !receivedAck) {
// check if inactive
if (millis() - lastActivity > resetPeriod) {
resetInactive();
}
return;
}
// continue on any success confirmation
if (sentAck) {
sentAck = false;
DW1000Ng::startReceive();
}
if (receivedAck) {
receivedAck = false;
// get message and parse
DW1000Ng::getReceivedData(data, LEN_DATA);
byte msgId = data[0];
if (msgId != expectedMsgId) {
// unexpected message, start over again
//Serial.print("Received wrong message # "); Serial.println(msgId);
expectedMsgId = POLL_ACK;
transmitPoll();
return;
}
if (msgId == POLL_ACK) {
timePollSent = DW1000Ng::getTransmitTimestamp();
timePollAckReceived = DW1000Ng::getReceiveTimestamp();
expectedMsgId = RANGE_REPORT;
transmitRange();
noteActivity();
} else if (msgId == RANGE_REPORT) {
expectedMsgId = POLL_ACK;
float curRange;
memcpy(&curRange, data + 1, 4);
transmitPoll();
noteActivity();
} else if (msgId == RANGE_FAILED) {
expectedMsgId = POLL_ACK;
transmitPoll();
noteActivity();
}
}
}
2-2 태그모듈용(거리계산 출력)
/*
* MIT License
*
* Copyright (c) 2018 Michele Biondi, Andrea Salvatori
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
* copies or substantial portions of the Software.
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
* SOFTWARE.
*/
/*
* Copyright (c) 2015 by Thomas Trojer <thomas@trojer.net>
* Decawave DW1000 library for arduino.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
* @file RangingAnchor.ino
* Use this to test two-way ranging functionality with two
* DW1000Ng:: This is the anchor component's code which computes range after
* exchanging some messages. Addressing and frame filtering is currently done
* in a custom way, as no MAC features are implemented yet.
*
* Complements the "RangingTag" example sketch.
*
* @todo
* - weighted average of ranging results based on signal quality
* - use enum instead of define
* - move strings to flash (less RAM consumption)
*/
#include <DW1000Ng.hpp>
#include <DW1000NgUtils.hpp>
#include <DW1000NgRanging.hpp>
/*
// connection pins
const uint8_t PIN_RST = 9; // reset pin
const uint8_t PIN_IRQ = 2; // irq pin
const uint8_t PIN_SS = SS; // spi select pin
*/
const uint8_t PIN_SCK = 18;
const uint8_t PIN_MOSI = 23;
const uint8_t PIN_MISO = 19;
const uint8_t PIN_SS = 2;
const uint8_t PIN_RST = 15;
const uint8_t PIN_IRQ = 5;
// messages used in the ranging protocol
// TODO replace by enum
#define POLL 0
#define POLL_ACK 1
#define RANGE 2
#define RANGE_REPORT 3
#define RANGE_FAILED 255
// message flow state
volatile byte expectedMsgId = POLL;
// message sent/received state
volatile boolean sentAck = false;
volatile boolean receivedAck = false;
// protocol error state
boolean protocolFailed = false;
// timestamps to remember
uint64_t timePollSent;
uint64_t timePollReceived;
uint64_t timePollAckSent;
uint64_t timePollAckReceived;
uint64_t timeRangeSent;
uint64_t timeRangeReceived;
uint64_t timeComputedRange;
// last computed range/time
// data buffer
#define LEN_DATA 16
byte data[LEN_DATA];
// watchdog and reset period
uint32_t lastActivity;
uint32_t resetPeriod = 250;
// reply times (same on both sides for symm. ranging)
uint16_t replyDelayTimeUS = 3000;
// ranging counter (per second)
uint16_t successRangingCount = 0;
uint32_t rangingCountPeriod = 0;
float samplingRate = 0;
device_configuration_t DEFAULT_CONFIG = {
false,
true,
true,
true,
false,
SFDMode::STANDARD_SFD,
Channel::CHANNEL_5,
DataRate::RATE_850KBPS,
PulseFrequency::FREQ_16MHZ,
PreambleLength::LEN_256,
PreambleCode::CODE_3
};
interrupt_configuration_t DEFAULT_INTERRUPT_CONFIG = {
true,
true,
true,
false,
true
};
void setup() {
// DEBUG monitoring
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
Serial.println(F("### DW1000Ng-arduino-ranging-anchor ###"));
// initialize the driver
DW1000Ng::initialize(PIN_SS, PIN_IRQ, PIN_RST);
Serial.println(F("DW1000Ng initialized ..."));
// general configuration
DW1000Ng::applyConfiguration(DEFAULT_CONFIG);
DW1000Ng::applyInterruptConfiguration(DEFAULT_INTERRUPT_CONFIG);
DW1000Ng::setDeviceAddress(1);
DW1000Ng::setAntennaDelay(16436);
Serial.println(F("Committed configuration ..."));
// DEBUG chip info and registers pretty printed
char msg[128];
DW1000Ng::getPrintableDeviceIdentifier(msg);
Serial.print("Device ID: "); Serial.println(msg);
DW1000Ng::getPrintableExtendedUniqueIdentifier(msg);
Serial.print("Unique ID: "); Serial.println(msg);
DW1000Ng::getPrintableNetworkIdAndShortAddress(msg);
Serial.print("Network ID & Device Address: "); Serial.println(msg);
DW1000Ng::getPrintableDeviceMode(msg);
Serial.print("Device mode: "); Serial.println(msg);
// attach callback for (successfully) sent and received messages
DW1000Ng::attachSentHandler(handleSent);
DW1000Ng::attachReceivedHandler(handleReceived);
// anchor starts in receiving mode, awaiting a ranging poll message
receiver();
noteActivity();
// for first time ranging frequency computation
rangingCountPeriod = millis();
}
void noteActivity() {
// update activity timestamp, so that we do not reach "resetPeriod"
lastActivity = millis();
}
void resetInactive() {
// anchor listens for POLL
expectedMsgId = POLL;
receiver();
noteActivity();
}
void handleSent() {
// status change on sent success
sentAck = true;
}
void handleReceived() {
// status change on received success
receivedAck = true;
}
void transmitPollAck() {
data[0] = POLL_ACK;
DW1000Ng::setTransmitData(data, LEN_DATA);
DW1000Ng::startTransmit();
}
void transmitRangeReport(float curRange) {
data[0] = RANGE_REPORT;
// write final ranging result
memcpy(data + 1, &curRange, 4);
DW1000Ng::setTransmitData(data, LEN_DATA);
DW1000Ng::startTransmit();
}
void transmitRangeFailed() {
data[0] = RANGE_FAILED;
DW1000Ng::setTransmitData(data, LEN_DATA);
DW1000Ng::startTransmit();
}
void receiver() {
DW1000Ng::forceTRxOff();
// so we don't need to restart the receiver manually
DW1000Ng::startReceive();
}
void loop() {
int32_t curMillis = millis();
if (!sentAck && !receivedAck) {
// check if inactive
if (curMillis - lastActivity > resetPeriod) {
resetInactive();
}
return;
}
// continue on any success confirmation
if (sentAck) {
sentAck = false;
byte msgId = data[0];
if (msgId == POLL_ACK) {
timePollAckSent = DW1000Ng::getTransmitTimestamp();
noteActivity();
}
DW1000Ng::startReceive();
}
if (receivedAck) {
receivedAck = false;
// get message and parse
DW1000Ng::getReceivedData(data, LEN_DATA);
byte msgId = data[0];
if (msgId != expectedMsgId) {
// unexpected message, start over again (except if already POLL)
protocolFailed = true;
}
if (msgId == POLL) {
// on POLL we (re-)start, so no protocol failure
protocolFailed = false;
timePollReceived = DW1000Ng::getReceiveTimestamp();
expectedMsgId = RANGE;
transmitPollAck();
noteActivity();
}
else if (msgId == RANGE) {
timeRangeReceived = DW1000Ng::getReceiveTimestamp();
expectedMsgId = POLL;
if (!protocolFailed) {
timePollSent = DW1000NgUtils::bytesAsValue(data + 1, LENGTH_TIMESTAMP);
timePollAckReceived = DW1000NgUtils::bytesAsValue(data + 6, LENGTH_TIMESTAMP);
timeRangeSent = DW1000NgUtils::bytesAsValue(data + 11, LENGTH_TIMESTAMP);
// (re-)compute range as two-way ranging is done
double distance = DW1000NgRanging::computeRangeAsymmetric(timePollSent,
timePollReceived,
timePollAckSent,
timePollAckReceived,
timeRangeSent,
timeRangeReceived);
/* Apply simple bias correction */
distance = DW1000NgRanging::correctRange(distance);
String rangeString = "Range: "; rangeString += distance; rangeString += " m";
rangeString += "\t RX power: "; rangeString += DW1000Ng::getReceivePower(); rangeString += " dBm";
rangeString += "\t Sampling: "; rangeString += samplingRate; rangeString += " Hz";
Serial.println(rangeString);
//Serial.print("FP power is [dBm]: "); Serial.print(DW1000Ng::getFirstPathPower());
//Serial.print("RX power is [dBm]: "); Serial.println(DW1000Ng::getReceivePower());
//Serial.print("Receive quality: "); Serial.println(DW1000Ng::getReceiveQuality());
// update sampling rate (each second)
transmitRangeReport(distance * DISTANCE_OF_RADIO_INV);
successRangingCount++;
if (curMillis - rangingCountPeriod > 1000) {
samplingRate = (1000.0f * successRangingCount) / (curMillis - rangingCountPeriod);
rangingCountPeriod = curMillis;
successRangingCount = 0;
}
}
else {
transmitRangeFailed();
}
noteActivity();
}
}
}
3. 테스트결과
- 비교적 안정적으로 거리 측정이 되고 거리 이동에 따라 실시간으로 변경되는 등 상당히 정확히 반응했지만 거의 근접했을 떄 음수값이 나오는 등 이상 현상이 발생된다. 모듈별 또는 MCU 기종에 따라 변화되는 내용을 Calibration 작업해 주여야 할 것을 보인다.
-다른 거리측정 방식에 비해 장점은 비교적 정확한 거리 측정이 가능하다는 점 이외에도 중간 장애물이 있어도 사용 가능하다는 것이다. 초음파,레이저에 의한 거리측정의 경우 중간 장애물이 있으면 장애물에서 반사되어 버리기 때문에 중간 장애물과의 거리가 측정되어 버리지만 UWB방식의 거리측정은 두 모듈간 패킷을 주고 받는 시간간격을 측정하여 계산하는 방식이기 때문에 중간장애물이 있어도 크게 영향을 받지 않는다. 실제로 한 모듈은 책상위 또 다른 모듈은 책상아래에 놓고 움직여 보아도 원만하게 거리 변동이 추적된다.
-제조사에서는 PCB내장안테나 만으로도 40m까지 측정가능하다고 하나 약간의 장매울에도 신호감도가 약해지는 것을 볼때 이것이 가능할 것인지는 의문이다. 다른 사용자들의 실험에 의하면 내장안테나 모델일 경우 탁트인 환경에서도 10미터 내외가 한계라는 것을 보아 실무에서 활용할 때에는 최소한 앵커 모듈에는 고출력 외장안테나를 사용하는 방식이 되어야 할 것으로 보인다.
'각종 부품 사용방법 > 통신 및 연결부품' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DWM1000( UWB통신모듈) 테스트 (0) | 2021.10.28 |
|---|---|
| DWM1000 (UWB통신모듈) 모듈의 소개 (3) | 2021.10.27 |
| UWB( Ultra Wide Band)통신 소개와 특장점 (1) | 2021.10.20 |
| HM-10 BLE 블루투스 통신모듈 사용법 (0) | 2021.07.13 |
| HC-06 클래식 블루투스 통신모듈 사용법 (0) | 2021.06.27 |
